Understanding Single-Phase Vs. Three-Phase Generators
Single-phase vs. 3-phase? Choosing the right generator type is critical, affecting uptime, efficiency and long-term operating costs. For large-scale operations, the choice between single-phase and 3-phase power is foundational. Whether you are running a data center, a manufacturing plant or a construction site, understanding the difference can prevent overload, reduce energy waste and keep your business moving without interruption.
The Difference Between Single-Phase vs. 3-Phase Generators
Although single-phase and 3-phase generators are both designed to provide electrical power, they operate on different principles and serve different applications. It is essential to match your generator to the load profile to protect your equipment, save energy and ensure reliability when you need it most.
Single-Phase Generators
A single-phase generator produces electricity using one alternating current (AC) waveform. It delivers power through two wires, one hot and one neutral, with voltage cycling between them in a pulsating delivery that experiences peaks and troughs. This setup is similar to standard residential power, delivering power in a single, fluctuating sine wave. Voltage typically runs at 120V or 240V, depending on the setup, and it’s ideal for light commercial loads or backup systems where demand is modest. Some generators offer a 240V split-phase voltage, where the generator’s windings are connected to support both single-phase 120V and split-phase 120/240V output for higher loads.
3-Phase Generators
What is a 3-phase generator? A 3-phase generator produces power through three ACs spaced 120 electrical degrees apart. It uses four wires — three hot and one neutral — to create a more balanced and continuous power supply. It produces three sine waves, delivering power in a constant rotating sequence, minimizing dips. 3-phase power can be 208V or 480V, depending on regional standards and needs. These systems are built for heavy-duty, high-demand environments, such as factories, hospitals or large-scale commercial facilities.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
When it comes to powering business-critical operations, the type of generator you choose should meet the demands of your equipment, facility size and operating conditions. Here is a closer look at single-phase vs. 3-phase generators, where each type fits and why one system dominates in commercial and industrial settings.
Single-phase generators are practical and can handle significant loads, but face challenges when they are wrongfully integrated with high-demand equipment. For that reason, they are common in settings where energy needs are predictable and relatively light:
- Retail shops and offices: A single-phase generator powers lighting, HVAC units, computers, point-of-sale systems and small appliances.
- Mobile applications: Compact single-phase is ideal for jobsite trailers, trucks and remote locations that don’t require large power loads.
- Small medical offices: Clinics or smaller medical offices use single-phase generators when they don’t rely on high-voltage diagnostic equipment.
3-phase generators are built for scale. They are the backbone of industrial and commercial operations requiring consistent, high-capacity power, such as:
- Industrial facilities and manufacturing plants: Environments relying on motors, compressors, pumps, conveyors and large equipment require constant torque and reliable power. It supports tools like robotic arms and reduces the risk of motor overheating.
- Data centers: Servers and cooling systems draw large, steady loads. 3-phase generators offer high power density, efficient load balancing and scalable infrastructure for expanding digital workloads.
- Hospitals and health care facilities: Critical power environments demand redundancy, precision and consistency. 3-phase generators can power life-support systems, work seamlessly with automatic transfer switches (ATS) for backup scenarios, and meet code and compliance standards in most jurisdictions.
- Construction sites: From tower cranes to large compressors, 3-phase generators can handle heavy-duty tools and high starting loads. They also deliver fuel-efficient runtime under demanding conditions.
- Agriculture and food processing: Large farms and agricultural facilities rely on 3-phase power to keep grain dryers, irrigation pumps and other equipment running for long hours in remote areas.
- Commercial buildings with central systems: Large buildings like malls, office towers and hotels use 3-phase generators for elevators, central air systems and power distribution across multiple zones.
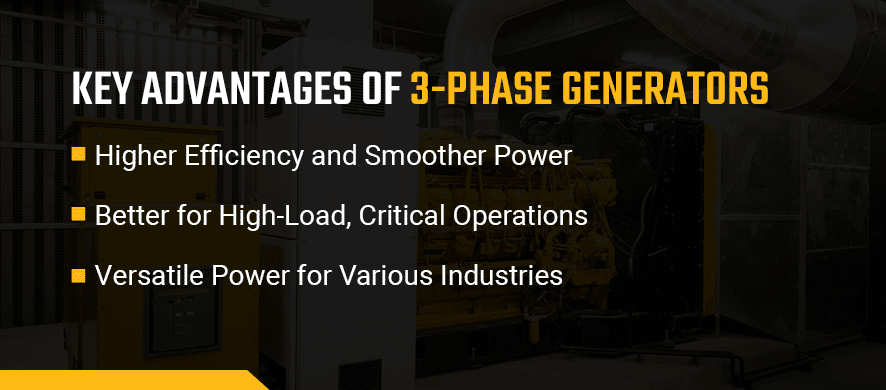
Key Advantages of 3-Phase Generators for Businesses
3-phase generators offer a smart, future-ready solution for businesses with high-demand equipment or critical operations. They are more efficient and more dynamic for broader applications in the long run, especially when uptime and performance are non-negotiable.
Higher Efficiency and Smoother Power
3-phase generators deliver power in a continuous, overlapping sequence across three alternating currents. This produces a more stable and balanced electricity flow, delivering less strain on motors, fewer power dips and improved overall performance.
Because power delivery is constant, 3-phase systems reduce heat buildup and energy loss, especially in large motors and industrial machines. That translates into higher energy efficiency, quieter operation and longer equipment life. It also means fewer interruptions and better voltage regulation, which is crucial for sensitive electronics and automated systems.
Better for High-Load, Critical Operations
From manufacturing floors to data centers, 3-phase generators are built to handle serious workloads. They support high starting currents and heavy running loads without compromising power quality or stability. Motors run cooler and more efficiently, which keeps critical systems like HVAC, production lines and server banks operating smoothly, even under pressure.
These abilities are especially valuable in sectors like food processing, health care and telecommunications, where even a brief power drop can cause equipment failure or data loss. With 3-phase power, businesses can support multiple large systems simultaneously, reduce overload risks and maintain performance across the board.
Lower Long-Term Operational Costs
While 3-phase generators often have a higher upfront cost, they pay off in long-term savings. First, they reduce energy waste and lower maintenance needs by minimizing mechanical and electrical stress. Equipment runs cooler, lasts longer and breaks down less frequently.
They also reduce infrastructure costs in many cases. For example, you can use smaller, more efficient wiring and circuit protection in a 3-phase setup. Moreover, because power is delivered more evenly, load balancing is easier, which helps avoid costly surges or imbalances that wear systems down over time.
Technical Considerations
Investing in a generator is a strategic decision directly affecting your operation’s efficiency and bottom line. Key factors to consider before making that investment include:
- Determining the size: Calculate the total load requirements, including peak demand and surge loads, to determine the size of the generator you need. Account for startup loads and factor in future expansion to avoid outgrowing the generator too quickly.
- Matching facility needs: Matching a generator is about voltage compatibility, phase requirements and transfer switching. The automatic transfer switch must be rated for your generator’s size and application.
- Integrating with the existing infrastructure: Proper integration ensures the generator synchronizes with utility power and is compatible with circuit breakers, grounding systems and load centers. Professional installation is nonnegotiable, as electrical codes vary by region.
- Compliance and life cycle management: Regulations affect everything from emissions to noise levels, which influence decision-making. Look for efficiency ratings, remote monitoring capabilities and maintenance plans to manage the generator’s life cycle better.
Always have a licensed electrician or generator specialist run a load analysis to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Explore Industrial and Commercial Generators From Woodstock Power
Generator selection and installation are best done by partnering with an experienced technician or generator specialist. These professionals can also help you decide between buying versus renting, based on time frame, deployment and core infrastructure needs.
With headquarters in Philadelphia, Woodstock Power operates nationwide. We offer commercial generators for rent or sale to accommodate short- or long-term needs. You can also find used generators at a much lower cost than retail pricing from us, or use our trade or upgrade options to increase your operation’s power demands. We also have emergency support and general maintenance services to help keep your business running.
Contact us online or at 610-658-3242 to find a generator solution that best fits your operations.
You can also follow us on Facebook, LinkedIn, X and YouTube for more information about commercial generators.