Advanced Backup Power Solutions for Hyperscale Data Centers

Hyperscale data centers can consume over 100 megawatts of power an hour. According to market research, hyperscale data center growth will only continue to explode, with an expected compound annual growth rate of 24.5% from 2025 to 2034. As the world expands digitally, even more significant levels of uninterrupted power will be required to sustain the data, artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing powered by hyperscalers.
A hyperscale data center is any large data center, typically spanning over 100,000 square feet. These data centers house essential IT equipment to support extensive workloads and optimize network infrastructure and connectivity. When power fails, organizations experience a range of ramifications, from financial losses to operational risks.
Investing in hyperscale data center backup power is an essential consideration, and traditional solutions may be on the way out.
The Escalating Growth and Power Demands of Hyperscale Data Centers
The growth of hyperscalers is rising quickly. At the end of 2024, the number of large data centers run by hyperscale providers was 1,136 — the United States makes up 54% of worldwide hyperscaler capacity. It’s predicted that 130-140 additional hyperscalers will come online yearly. The main drivers of hyperscale data center growth include:
- Generative AI: AI applications, such as image generation and code completion, require hyperscale infrastructure to handle complex algorithms and vast datasets. As generative AI becomes more widely used, the demand for hyperscaler resources will continue to rise.
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices: IoT devices, such as smart home gadgets and industrial sensors, rely on hyperscalers for extensive processing capabilities. These data centers are large enough to handle data from billions of IoT devices.
- Social media: From X to Facebook to YouTube, social media platforms process huge amounts of user-generated content. These websites require the power of hyperscale data centers, which provide enough storage, bandwidth and processing capacity to support constant uptime and network connectivity.
- Cloud services: More organizations are steadily moving toward cloud infrastructures. This kind of computing needs the bandwidth of large data centers to deliver on-demand computing resources and storage.
These applications all require extensive power. For example, some researchers estimate that the AI industry will consume as much energy as a country the size of Argentina by 2027. In the U.S., data center power consumption is set to account for almost half of the electricity growth demand between now and 2030. A large portion of that consumption isn’t even for powering the servers or hardware — it’s for the cooling systems, which are necessary to avoid potential failure.
The Critical Need for Advanced Backup Power
For owners and operators of hyperscalers, power resilience is a significant concern. If the main power sources fail, the consequences worsen with every moment of downtime. Between financial losses, reputational damage, safety risks and regulatory penalties, even brief power outages can leave teams scrambling.
The concept of redundancy is central to supporting hyperscale data centers, which are considered Tier 4 data centers. These data centers require extremely high levels of reliability, often aiming for seven “9s,” or 99.99999% uptime. This endeavor includes having backup power sources, redundant network connections, multiple cooling systems and replicated data storage. The goal is to eliminate single points of failure so if one component fails, another can immediately take over, minimizing downtime.
In a power outage, backup systems provide an alternate power source to keep the data center running without interruption. These systems typically include a combination of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and backup generators. If the grid fails, the UPS immediately begins supplying short-term battery power as a transition point before the backup generators switch on. These generators continue providing power until the primary power sources are restored and operational.
Given the increasing demands on hyperscale data centers, relying solely on traditional backup power solutions may no longer be sufficient. To minimize risk as much as possible, hyperscalers can invest in the next generation of backup power, providing greater reliability, efficiency and sustainability.
Hyperscale Data Center Trends in Backup Power Solutions
Historically, data centers have mainly relied on diesel generators for backup power. When the main power source fails, diesel generators are easy to deploy and provide reliable electricity, minimizing center downtime. However, they aren’t without their drawbacks.
One of the biggest concerns is their environmental impact. These generators produce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants, and they’re considerably noisy. Additionally, operating diesel generators often involves navigating a complex web of regulations and permitting requirements, which can be time-consuming and costly.
As hyperscalers draw more power and environmental regulations become stricter, the challenges associated with diesel generators are only likely to increase. Choosing advanced generators and other solutions for hyperscale data centers is the next logical step:
1. Modern Diesel Generators
It’s important to note that diesel generators are still a reliable, widely used option, especially for long-duration outages. The good news is that they’re advancing in different ways to minimize their drawbacks. In particular, today’s diesel generators provide improved fuel efficiency, lower emissions and higher power density.
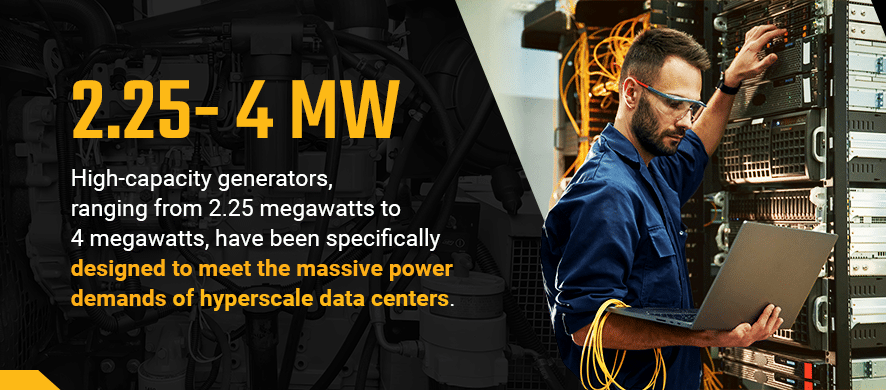
High-capacity generators, ranging from 2.25 megawatts to 4 megawatts, have been specifically designed to meet the massive power demands of hyperscale data centers. These advanced generators offer increased reliability and performance, making them a viable option for facilities requiring significant backup power capabilities.
2. Natural Gas Generators
These generators offer a cleaner-burning, efficient alternative to diesel generators, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and potentially lowering operating costs. Plus, fuel delivery and storage aren’t an issue since natural gas is readily available in the existing gas grid.
Some major tech companies are already incorporating natural gas into their data center power strategies. For example, Microsoft has been exploring natural gas fuel cells for its data centers, citing their potential for reduced emissions and improved energy efficiency.
For hyperscalers, natural gas generators are becoming increasingly popular to supply reliable backup power while meeting sustainability goals.
3. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
Unlike traditional generators, which require time to start up, BESS can provide power within milliseconds. This capability offers instantaneous backup power and improves power quality for hyperscale data centers. Advancements in battery technology, such as lithium-ion, are making BESS more viable for large-scale applications.
Companies like Google use batteries for data center backup and grid stabilization services. As of 2025, Google has 100 million lithium-ion cells in its data centers. BESS can also be integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, to create a more sustainable and resilient power infrastructure.
4. Hydrogen Fuel Cells
As a clean energy solution for backup power in hyperscale data centers, hydrogen fuel cells provide high levels of efficiency with zero emissions — only heat and water are created as byproducts. These cells convert the chemical energy of hydrogen into electricity, providing a sustainable power source.
While green hydrogen production can be costly and limited in availability, ongoing development is making it a viable power source, even for hyperscalers. For instance, Microsoft has announced pioneering green hydrogen pilot projects to power its data centers.
5. Modular and Scalable Systems
These systems are one of the top hyperscale data center trends and are gaining traction. These systems allow operators to add or remove power units as demand shifts, optimizing efficiency. As data centers continue to see massive growth and power demands rise, modular setups can provide the necessary scalability and redundancy. If one unit fails, the others can automatically compensate, supporting continuous operation.
Contact Woodstock Power for Advanced Backup Power Solutions
Woodstock Power understands that data centers have complex needs, regardless of size. For decades, we’ve supported data centers with reliable, high-quality generator and power supplies sales from the industry’s leading brands.
Based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, we can support local businesses and customers nationwide. Let our knowledgeable, professional team help you find the right solutions for your hyperscale data center power consumption needs.
Learn more about our hyperscaler solutions to see how we can assist you today.